A Simple and Straightforward Process Mapping Example

Designed as an instructional resource, this case study provides a detailed process mapping example through the fictional company "Innovare Technologies" to demonstrate the practical application of business process mapping. It mirrors the real-world complexities—like operational bottlenecks, system integration issues, and lack of standardization—often encountered in actual process improvement initiatives.
The narrative follows a logical progression from problem identification and analysis to solution design and implementation, providing a clear, realistic example for professionals, students, and teams seeking to understand and apply BPM principles effectively.
Context and Background
Innovare Technologies is a growing mid-sized company that operates in the highly competitive sector of customized digital solutions. With a diverse portfolio of clients across multiple industries and a commitment to delivering tailored software products, the company has undergone a rapid expansion in recent years. As this growth unfolded, new challenges emerged—primarily related to the scalability of internal operations, the consistency of service delivery, and the visibility of cross-departmental workflows.
Although Innovare had a capable and committed workforce, the absence of standardized processes, combined with disconnected systems and informal practices, began to create friction in the operation. Decision-makers noticed an increase in project delivery delays, client dissatisfaction due to service inconsistencies, and an overload of manual work in several departments. These issues, though diverse in appearance, shared a common root cause: the company lacked a unified understanding of how its internal processes truly worked across functions.
In response, Innovare’s executive leadership approved a company-wide initiative to map, analyze, and optimize business processes, aiming not only to resolve current inefficiencies but also to establish a strong foundation for long-term operational excellence and digital transformation.
1. Strategic Alignment and Initiative Kick-Off
From the beginning, the leadership team positioned the initiative not as a side project, but as a core strategic effort to support the company’s next growth phase. The project was entrusted to the Process and Quality Management Department, which would coordinate the work alongside the IT team and managers from all operational departments.
Several objectives were clearly defined in the project charter:
- To provide complete visibility of end-to-end business processes;
- To identify bottlenecks, redundancies, and unnecessary complexities;
- To increase operational efficiency by eliminating waste;
- To ensure that internal processes align with external client expectations and compliance requirements;
- To create a baseline for implementing automation and digital tools;
- To establish measurable indicators for continuous performance monitoring.
The project team chose to follow a structured and iterative methodology based on best practices in Business Process Management (BPM), encompassing the full process lifecycle: process identification, documentation, modeling, critical analysis, redesign, implementation, and monitoring. The BPMN 2.0 (Business Process Model and Notation) standard was selected as the visual modeling language to ensure clarity, standardization, and scalability.
2. Process Identification and Document-Based Validation
The first major phase of the project focused on identifying and documenting the company's key business processes. This effort was carried out through a combination of methods designed to triangulate information and ensure a complete and accurate understanding of current operations.
Approach and Data Collection
The team conducted:
- Structured interviews with managers and frontline staff across all departments;
- Observation sessions to witness real workflows in practice;
- Collaborative workshops, where cross-functional teams walked through their current activities and discussed handoffs between teams.
From this effort, the team identified and prioritized several macroprocesses across four main areas of the organization:
- Customer Service: Managing customer inquiries, issue resolution, post-sales communication;
- Project Development: From client request intake to solution delivery and project closure;
- Logistics and Delivery: Planning, execution, and monitoring of physical or digital deliveries;
- Administration and Finance: Budget control, invoicing, procurement, compliance, and financial planning.
Each department was asked to describe its processes end-to-end, capturing all key inputs, internal tasks, decisions, systems involved, outputs, and performance indicators used to monitor results.
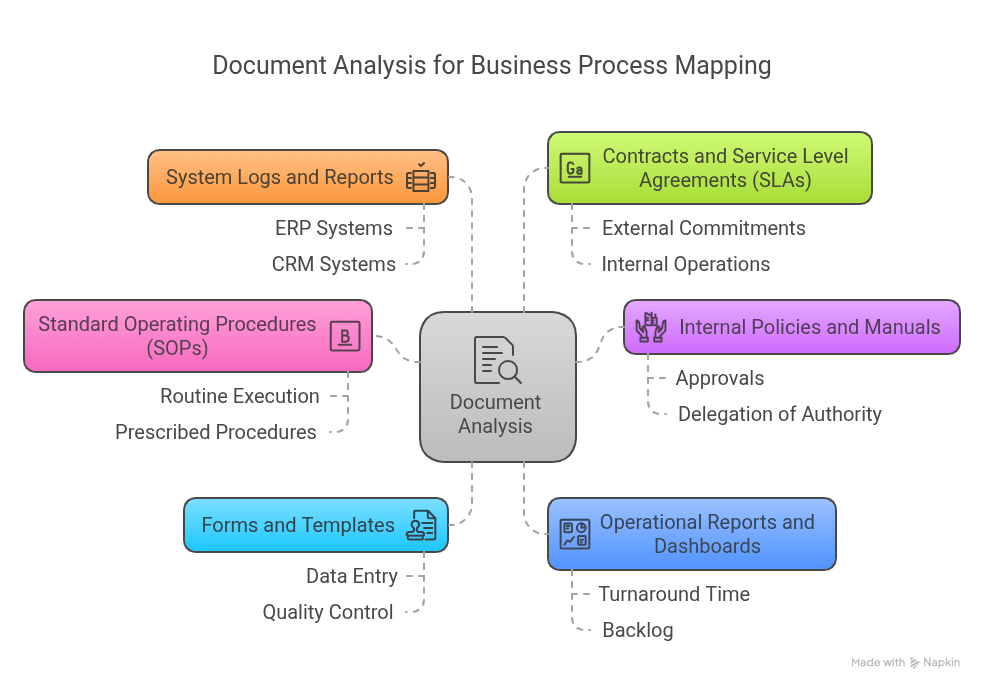
Document Analysis: Internal Standards and Governance Artifacts
A key part of this phase was the analysis of internal documentation, which helped validate the alignment (or misalignment) between formal processes and actual practices.
Documents reviewed included:
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): To understand what was officially prescribed in routine execution;
- Internal policies and manuals: Governance rules related to approvals, delegation of authority, procurement, and service levels;
- Forms and templates: Used for data entry, approvals, and quality control;
- Operational reports and dashboards: Offering insight into real-time performance metrics, such as turnaround time and backlog;
- System logs and reports: Extracted from the company’s ERP and CRM systems to trace real execution patterns;
- Contracts and Service Level Agreements (SLAs): To understand external commitments that influence internal operations.
This analysis allowed the team to compare “formal expectations” against the actual state of practice, revealing cases where processes were informal, undocumented, outdated, or inconsistent across teams. It also helped establish a baseline for updating and standardizing documentation company-wide.
3. Process Modeling and Organizational Clarity
Once the relevant information was collected and validated, the team transitioned into the process modeling phase. The goal was not only to create accurate representations of how processes worked but also to align internal understanding and enable efficient collaboration among different teams.
Standardization Through BPMN
All process models were created using BPMN 2.0, which provided a precise and industry-standard way to map events, tasks, decisions, and flows.
To ensure clarity and usability, the models adhered to the following conventions:
- Processes were visualized in swimlanes to delineate responsibilities between departments or systems;
- Decisions were explicitly modeled using gateway symbols to show conditional flows;
- Activities followed consistent naming standards, using action-oriented descriptions;
- External stakeholders (e.g., customers, suppliers) and systems (e.g., CRM, ERP) were represented explicitly to identify integration points.
👉 Want to learn how to draw a BPMN diagram? Explore our step-by-step guide to creating clear and effective process models.
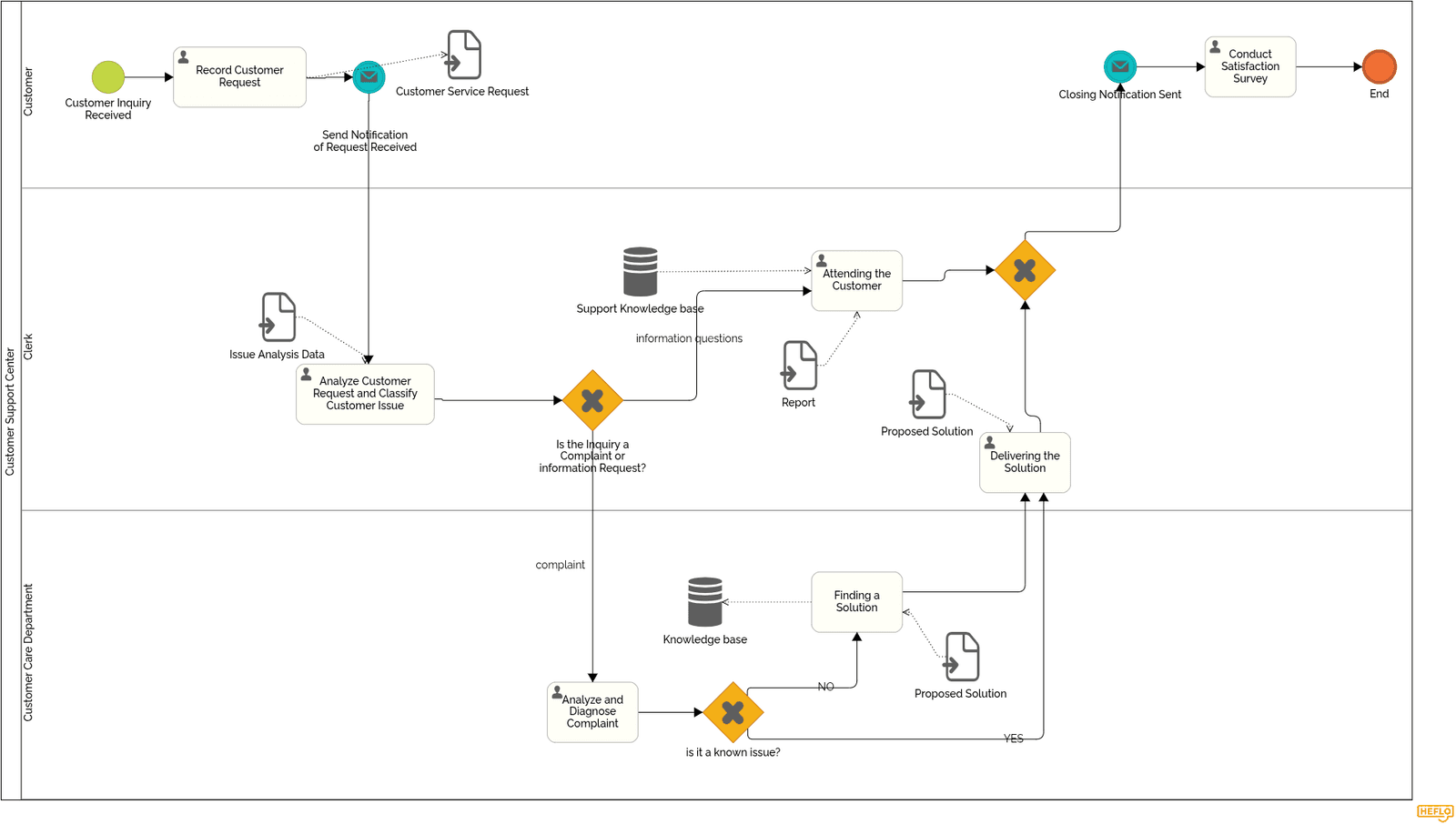
Customer Service Process – A Detailed Example
One of the early processes modeled was the Customer Service workflow, which included:
- Intake of service requests via multiple channels;
- Logging and categorization of the request in the CRM system;
- Triage and routing to the appropriate internal area (technical support, billing, etc.);
- Resolution by the responsible team;
- Communication with the customer and case closure;
- Feedback and post-case quality check.
This process was modeled with clearly defined roles, dependencies, and expected turnaround times for each step.
🧠 Explore the full Customer Service process diagram—open it in the HEFLO BPMN modeler and listen to our podcast episode for extra insights.
Validation and Team Involvement
Each modeled process was then reviewed and validated in a collaborative session with the departments involved. This step was critical not only for ensuring accuracy but also for building ownership and promoting organizational learning.
Many employees reported that this was the first time they had seen a full end-to-end view of how their work connected with others in the company—a powerful outcome that strengthened cross-functional alignment.
4. Critical Process Analysis and Improvement Design
With the models in place, the team conducted a comprehensive analysis to identify performance gaps and redesign opportunities. This step combined both quantitative data and experiential knowledge from operational teams.
Diagnostic Techniques Used
- Value Stream Analysis: Used to identify value-adding versus non-value-adding activities;
- Cycle Time and Cost Analysis: Leveraging historical data to quantify performance;
- Bottleneck Identification: Pinpointing tasks with the highest delays or queues;
- Risk Assessment: Identifying process steps with compliance, operational, or reputational risk;
- Voice of the Employee (VoE): Gathering qualitative insights from frontline staff.
Findings and Patterns
Several recurring issues were identified:
- Multiple approvals performed manually without clear criteria or authority delegation;
- Data entered redundantly into different systems due to lack of integration;
- Missing service level agreements between departments, leading to delays and miscommunication;
- Inconsistent handling of exceptions due to the absence of standardized procedures;
- Repetitive, rule-based tasks suitable for automation but still executed manually.
Prioritization of Improvements
The team categorized improvement opportunities based on effort vs. impact to guide implementation strategy. Quick wins were targeted for immediate execution, while more complex changes were included in a roadmap for medium- and long-term transformation.
5. Implementation and Governance of New Processes
Once solutions were prioritized, the organization moved into implementation mode—ensuring that redesigned processes were deployed with proper support, training, and monitoring structures.
Three Dimensions of Execution
a) Process Redesign and Simplification
Process flows were streamlined, reducing the number of handoffs, approvals, and unnecessary steps. Key processes were restructured with clearly defined decision rules and escalation paths.
b) Technology Integration and Automation
- BPMS, ERP, and ticketing systems were integrated;
- Automated workflows were created using RPA bots and internal tools;
- Dynamic forms were developed to enforce business rules at the data-entry point.
c) People Enablement and Standardization
Updated documentation was released across the organization, including:
- New SOPs reflecting redesigned flows;
- Checklists and templates for key operational activities;
- Team training sessions focused on role clarity, performance expectations, and practical use of the new models.
Monitoring and Continuous Improvement
To ensure sustained value delivery, a governance model was established:
- KPIs tracked performance at the process level (e.g., turnaround time, SLA compliance, rework);
- Dashboards provided real-time visibility to managers and teams;
- Regular process performance meetings were scheduled;
- Feedback channels allowed for continuous refinement and small-scale improvements.
6. Tangible Results and Organizational Impact
After three months of implementation, Innovare was able to capture a series of measurable and qualitative improvements.
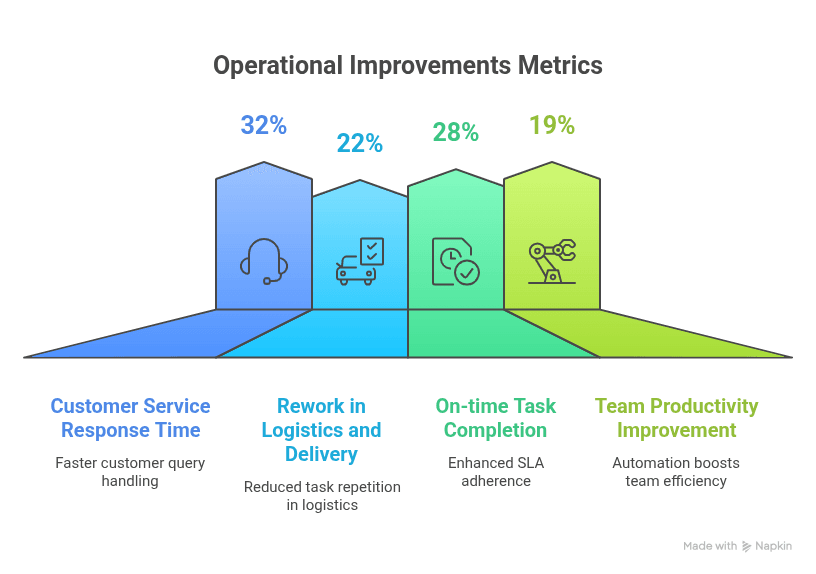
Quantitative Results
- 32% reduction in customer service response time;
- 22% reduction in rework within logistics and delivery;
- 28% increase in on-time task completion (SLA compliance);
- 19% improvement in team productivity due to automation of repetitive tasks.
Qualitative Impact
- Improved cross-functional collaboration and role clarity;
- Stronger internal alignment around how value is delivered to customers;
- Reduced operational risk through formalized procedures and controls;
- Increased employee engagement with a shared sense of ownership and transparency;
- Solid foundation for future automation, analytics, and performance-based management.
7. Strategic Conclusion and Lessons Learned from the Process Mapping Example
The Innovare case demonstrates that business process mapping, when approached strategically, serves as a catalyst for broad organizational transformation. Rather than being a purely technical exercise, the initiative drove alignment across teams, clarified responsibilities, supported cultural change, and enabled smarter decision-making.
Key Takeaways for Practitioners
- Multiple data sources lead to better insights: Combining interviews, observation, and documentation creates a complete picture.
- Modeling adds value beyond visuals: Standardized models foster collaboration and drive shared understanding.
- Change requires more than automation: Simplifying decisions and clarifying responsibilities often bring bigger gains than just deploying new tools.
- Monitoring is not optional: KPIs and governance mechanisms are vital to sustaining results.
- People are central: Engagement, communication, and training determine the real success of process transformation.
This exploration demonstrates that business process mapping is a dynamic strategic asset, not just a static record. It enables organizations to gain crucial self-awareness, focus on value creation, and persistently evolve towards greater efficiency. The journey from workflow analysis to process redesign and performance tracking unlocks tangible results and fosters long-term transformation. For teams ready to align, simplify, and improve with confidence, embracing process mapping is a foundational step towards enduring operational excellence.
🌟 Interested in going further? Read our next article on business process documentation and learn how to create clear, structured records that support consistency and compliance.
